Methadone Drug Information
Classification
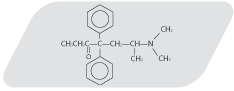 Methadone is a narcotic analgesic which is approximately equipotent to that of morphine.
Methadone has been utilized to treat opioid dependency and prescribed as a heroin substitute in methadone maintenance programs since the 1960's. Typically, daily oral dosing with doses up to 180 mg/day,
is prescribed with efficacy measured by the absence of withdrawl symptoms. Dosing is then gradually decreased until opiate dependency is eliminated.
Methadone is a narcotic analgesic which is approximately equipotent to that of morphine.
Methadone has been utilized to treat opioid dependency and prescribed as a heroin substitute in methadone maintenance programs since the 1960's. Typically, daily oral dosing with doses up to 180 mg/day,
is prescribed with efficacy measured by the absence of withdrawl symptoms. Dosing is then gradually decreased until opiate dependency is eliminated.
Metabolism
Methadone is metabolized to several metabolites with EDDP being one of the more prominent ones.. Monitoring for the presence of EDDP (methadone metabolite) is a means to determine compliance to methadone treatment. Large individual variations in elimination do occur due to urine pH, urine volume, dose, rate of metabolism, and drug interactions. Methadone can be detected in the urine 2-13 days after use.
Laboratory drug testing: Methods of Analysis
Immunoassays, such as enzyme immunoassay (EIA) are common methods for detecting methadone and methadone metabolite (EDDP) in urine. Confirmation of presumptive positive urines should be performed by specific methods such as gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS) or liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS).
800-255-2159
RTL also offers on-site test devices. Click here to view the complete line of Reditest® screening devices.
Drug information data is not definitive and should be used for reference guidelines only.